An auto mains failure (AMF) system is a crucial automation technology used to ensure uninterrupted power supply in facilities that cannot afford downtime. Found in hospitals, data centers, telecom sites, and industrial plants, these systems automatically detect power outages and start backup generators — restoring power within seconds.
In this comprehensive technical guide, we break down exactly how auto mains failure systems work, the components involved, wiring logic, signal flow, protection features, and real-world applications. Whether you’re an engineer, technician, or facility manager, this article gives you the deep technical insight you need.
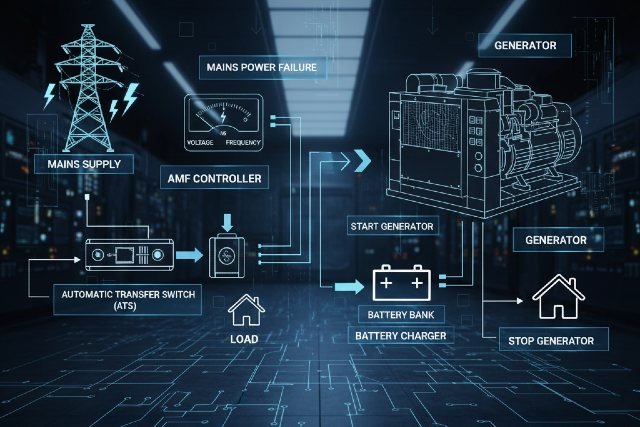
What Is an Auto Mains Failure (AMF) System?
An auto mains failure system (also called an automatic mains failure panel) is an intelligent control mechanism that:
- Monitors the incoming utility (mains) supply
- Detects power failure, voltage fluctuations, or phase loss
- Automatically starts the diesel generator (DG) set
- Transfers load from mains to generator
- Keeps monitoring generator parameters
- Re-transfers load back to mains once stable
- Shuts down the generator safely
Essentially, it automates the entire power continuity cycle without human intervention.
How Auto Mains Failure Systems Work: Step-by-Step Operation
Below is a precise sequence of how an AMF panel operates during normal, failure, and restoration scenarios.
1. Monitoring the Mains Supply (Normal Mode)
The AMF system continuously monitors:
- Voltage levels
- Frequency
- Phase sequence
- Phase presence
- Neutral stability
Normal operating parameters typically include:
| Parameter | Acceptable Range |
|---|---|
| Voltage | 380–415V (three-phase), 220–240V (single-phase) |
| Frequency | 50/60 Hz ± 2% |
| Phase | Balanced, correct sequence |
If mains is stable, the AMF:
- Keeps the load connected to the mains
- Keeps the generator off
2. Detecting a Power Failure
When the system senses any abnormality:
- Under-voltage
- Over-voltage
- Phase failure
- Frequency deviation
- Complete blackout
…it activates the programmed mains failure delay (typically 3–10 seconds to avoid false triggers).
Once confirmed, the AMF initiates generator auto-start.
3. Starting the Generator Automatically
The AMF sends a signal to the generator’s engine control module (ECM) or starter motor.
It performs:
- Fuel solenoid activation
- Starter crank attempt (3–5 cycles, each 5–10 seconds)
- RPM monitoring
- Oil pressure and temperature check
- Stability verification
If the generator fails to start after all attempts, the panel triggers a GEN FAIL alarm.
4. Load Transfer to Generator Supply
Once the generator reaches stable conditions — typically rated voltage and frequency — the AMF:
- Opens the mains circuit breaker (MCB/MCCB/ACB)
- Closes the generator circuit breaker (GCB)
This is usually done through:
- Motorized breakers
- Electromagnetic contactors
- Automatic transfer switches (ATS)
The load now runs on generator power.
5. Continuous Monitoring During Generator Mode
While running on generator supply, the AMF measures:
- Generator voltage
- Frequency
- Phase balance
- Oil pressure
- Coolant temperature
- Fuel level
- Battery voltage
Any abnormality triggers alarms such as:
- Generator overload
- Low oil pressure
- High engine temperature
- Under-frequency
- Over-voltage
The AMF may shut down the generator depending on severity.
6. Mains Power Restoration Detection
The AMF keeps monitoring the mains supply even while on generator mode.
When the mains returns, it checks for:
- Stable voltage
- Balanced phases
- Correct frequency
If stable for a programmed period (10–30 seconds), the AMF prepares to transfer load back.
7. Re-Transfer Back to Mains Supply
The system executes:
- Open Generator Breaker (GCB)
- Close Mains Breaker (MCB/ACB/ATS)
Load is now back on utility power.
8. Cooling and Shutdown of Generator
After transferring load, the AMF enables a gen-set cooling cycle (1–3 minutes) to protect:
- Turbocharger
- Engine block
- Fuel system
Then the AMF shuts down the generator safely and resumes standby mode.
Main Components of an AMF System
An auto mains failure system includes both electrical and electronic components.
1. Control Unit / Relay Module
The brain of the AMF system.
Functions:
- Voltage sensing
- Frequency monitoring
- Auto-start/stop logic
- Breaker control
- Fault detection
Common models:
- Deep Sea Electronics (DSE) 7320
- ComAp AMF25
- SmartGen HGM6120
2. Circuit Breakers / Contactors
Used for load switching:
- Mains supply breaker (MCCB/ACB)
- Generator supply breaker
- Interlocking system to prevent back feeding
Breakers ensure safe load transfer.
3. Sensors and Feedback Devices
- Voltage sensors
- Current transformers (CTs)
- Oil pressure switches
- Temperature sensors
- Battery chargers
- Fuel level sensors
4. Generator Starter Mechanisms
- Starter motor
- Fuel pump
- Glow plugs (for cold climates)
5. Wiring Harness / Control Cables
Low-voltage control wires run between:
- AMF panel
- Generator
- ATS
These include:
- Start/stop wires
- Feedback signals
- Emergency stop inputs
Wiring Diagram Preview
Include an image named auto-mains-failure-wiring-diagram.png
Benefits of Auto Mains Failure Systems
1. Instant Power Continuity
Restores power within seconds — critical for hospitals, servers, and factories.
2. Full Automation
No operator needed for generator start/stop.
3. Equipment Protection
Avoids damage from brownouts, phase failures, and unstable utilities.
4. Safety Enhancement
Eliminates back-feeding and manual switching risks.
5. Fuel Efficiency and Engine Protection
Cool-down cycles and optimized start attempts extend generator life.
Common AMF System Applications
- Hospitals and Emergency Rooms
- Data Centers
- Telecom Towers
- Industrial Plants
- Cold Storage Facilities
- Commercial Buildings
- Government Institutions
Difference Between AMF and ATS
| Feature | AMF | ATS |
|---|---|---|
| Detects mains failure | ✔ | ✔ |
| Starts generator automatically | ✔ | ✘ (unless paired with AMF) |
| Transfers load | ✔ | ✔ |
| Handles engine monitoring | ✔ | ✘ |
Quick Summary:
An AMF panel controls the generator, while an ATS controls the load transfer. Many modern systems combine both.
FAQs (Optimized for Featured Snippets)
What is an auto mains failure system?
An auto mains failure system automatically starts a backup generator and transfers load when the mains supply fails.
How does an AMF panel detect power failure?
It continuously monitors voltage, frequency, and phase parameters. When they fall outside preset limits, it triggers generator start.
Is AMF the same as ATS?
No. AMF manages generator start/stop. ATS handles load transfer between mains and generator.
How long does an AMF system take to start a generator?
Most generators start within 5–15 seconds after mains failure detection.
Conclusion
An auto mains failure system is an essential automation solution for any facility that requires continuous power. By detecting mains failure, auto-starting the generator, transferring load, monitoring supply quality, and restoring power safely, AMF systems deliver seamless power continuity with high reliability.
Whether you’re designing a backup power solution or upgrading an existing system, understanding how auto mains failure systems work ensures better performance, reliability, and safety in your electrical infrastructure.













Leave a comment